How Should a Safe and Effective COVID‑19 Vaccine be Allocated? Health Economists Need to be Ready to Take the Baton
September 28, 2020
Laurence S. J. Roope1 · John Buckell1 · Frauke Becker1 · Paolo Candio1 · Mara Violato1 · Jody L. Sindelar2 · Adrian Barnett3 · Raymond Duch4 · Philip M. Clarke1, 5
Recently, there have been encouraging commitments around the world to manufacture coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines in anticipation of results from clinical studies. Although in stark contrast to the normal process of vaccine development, this unprecedented approach seems appropriate [1]. Every extra month spent without a COVID-19 vaccine comes at a substantial cost to both global public health and the economy, making it almost impossible to overspend on the research, development and production of a vaccine [2].
The logistics of universal vaccination are extremely challenging. In the UK, AstraZeneca plans to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Oxford University [3] with the aim of producing “30 million doses of the vaccine for the UK market by September, with expectations of 100 million doses by the end of the year” [4]. In total, AstraZeneca is committed to manufacturing 2 billion doses, including a licence with the Serum Institute of India for the supply of 1 billion doses, intended mainly for low-and middle-income countries and including at least 400 million by the end of 2020 [5]. The accelerated development has been assisted by prepurchase agreements from governments in several developed countries [6]. Other pharmaceutical companies have similar plans for manufacturing and stockpiling other vaccines currently in development [7]. While such planning is encouraging, if an effective vaccine does emerge, significant allocation challenges lie ahead. In this article, we outline these challenges and propose a framework to address them.
The timing of vaccine results is subject to considerable uncertainty. Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of vaccines need to recruit sufficient numbers of people to have statistical power to detect efficacy and potentially rare and/or delayed adverse effects. Uncertainty over future case numbers has led some RCTs to recruit participants from multiple countries [8]. Furthermore, the timing of announcements of the results of vaccine RCTs may be governed by reaching predefined stopping criteria, rather than occurring at a predetermined time. It is therefore probable that at the time the results of a successful vaccine RCT become known, most countries will have insufficient stockpiles to cover all those who would ideally be vaccinated. As a recent article noted, “As soon as the first COVID-19 vaccines get approved, a staggering global need will confront limited supplies” [9]. Furthermore, unlike other vaccines, there will be an expectation that “a COVID-19 vaccine should rapidly be delivered to the public as soon as rigorous testing has been completed, and efficacy and safety have been established” [10].
There will be competition both between and within countries for limited vaccine supplies. Issues surrounding the international distribution of a vaccine are of prime importance [11]. They have been the focus of both discussion [12] and initiatives such as COVAX, an international effort to make a range of potential vaccines available worldwide, including low- and middle-income countries [9]. Decisions on prioritisation are needed in advance so that allocation can begin immediately after an effective COVID-19 vaccine is approved for use by regulators. Alongside global initiatives, there is increasing recognition of the importance of deciding at a national level how best to allocate the available vaccine [13, 14]. Governments without a clear plan may be forced into quick decisions that favour politically well-connected groups instead of establishing clear, consistent evidence-based guidelines for the fair and equitable distribution of a COVID-19 vaccine [15].
At a national level, governments face a sequence of decisions (see Fig. 1). First, should vaccines be sold in private markets, alongside their public distribution? In most countries, citizens are entitled to gain preferential access to many medicines by allowing private purchase, alongside public schemes such as the UK’s National Health Service. However, some have likened the COVID pandemic to a war-time situation [16], where many goods, including health care, may be rationed [17]. On this basis, a government may opt for an entirely public framework for rationing the allocation of the vaccine and prohibit its private purchase. Even where governments allow individual purchase, they may consider price regulation and will need to put in place mechanisms to track and verify private vaccine use.
A standard framework for evaluating vaccines is cost effectiveness [18]. In the UK, for example, this is overseen by the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI), the expert body responsible for advising the UK Government [19]. This framework is likely to require considerable adaptation in order to be relevant to decisions regarding the allocation of a safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine. A more informative application of economic evaluation is likely to be in determining the relative net benefits of vaccinating different population subgroups.
Prioritisation of access is likely to be based on a number of criteria. For example, in interim advice, the JCVI has already indicated prioritisation of frontline health and social care workers in the allocation of a vaccine due to them being at “increased personal risk of exposure to infection with COVID-19” [20]. However, if occupational risk is the basis of prioritisation, then many other workers (e.g. bus drivers) face work-related exposure, which should be considered in a more comprehensive prioritisation exercise. Moreover, continuing lockdown is having such a detrimental economic impact [21] that there is a strong argument for considering productivity losses, which are not usually counted in the evaluation of vaccines for other diseases [22]. This could conceivably mean giving a relatively high priority to young economically active people, or to teachers to enable children to safely return to schooling and their parents to return to work.
Given the expected initial limits on vaccine supply, it is very likely that choices will need to be made based on a number of different criteria:
- Individual health benefits: Ideally, this would take into account trial results on efficacy and adverse effects, and model the implications of using the vaccine for different individuals or groups within the general population. Given the emerging evidence on the relative risk of mortality based on databases such as the UK Biobank [23], it should be possible to estimate potential quality-adjusted life-years gained [24].
- Societal health benefits: Susceptible, infected and recovered (SIR) models [25] that take into account the level and nature of population mixing could help to quantify the likely positive externalities associated with a vaccination programme. For example, those caring for elderly relatives may gain only a small individual benefit, but their vaccination may prevent COVID-19 in the individuals they are looking after.
- Benefits to the economy: There are several methods [26, 27] to estimate productivity losses from the COVID- 19 pandemic, and these could potentially be adapted to quantify the economic gains from different vaccination coverage strategies.
The prioritisation framework will need to account for outcomes in multiple dimensions. For example, determining the overall benefits of vaccinating those working in the retail and service sector may entail taking into account the (1) individual health benefits to staff; (2) societal health benefits via lower transmission to shoppers; and (3) benefits to the economy (e.g. from allowing more shops to open).
A prioritisation framework could also consider the equity implications of potential vaccination programmes. Here, decision makers could employ well-developed metrics for quantifying inequalities in access [28], and an emerging toolkit for incorporating equity and efficiency in economic evaluation [29].
Once the criteria have been finalised and existing evidence used to determine the impact of different vaccination strategies, then multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) [30] can be employed. This can involve applying weights to different criteria in order to rank alternatives. In the context of a vaccine, the objective would be to determine how different individuals should be ranked in order of priority.
One application of an MCDA-type approach could be to assign every individual a score or category indicating the extent to which they should be prioritised for vaccination. This would have some similarities with points-based systems used by governments for prioritisation in other contexts [31]. Another approach is to prioritise whole groups (e.g. all frontline public transport workers) based on average scores >of individuals within these groups.
The cost and efficiency of rolling out a vaccination programme (e.g. administration at the workplace versus health care facilities) may also influence prioritisation strategies. Another issue will be coverage. As a recent survey of seven European countries has highlighted [32], a significant proportion of the population (18.9%) indicate that they are unsure whether they want to get vaccinated, and therefore policy effort will be required to ensure adequate vaccination rates.
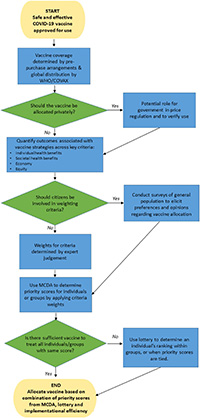
Fig. 1
Decisions for governments in allocating a vaccine. MCDA multicriteria decision analysis.
Click here to view full-size.
One way of informing how criteria should be weighted would be to seek the preferences of citizens, e.g. via nationally representative surveys. This could involve asking or eliciting (e.g. through choice experiments) the general population’s ranking of the relative importance of different types of outcomes associated with a COVID-19 vaccination programme, such as health versus economic benefits [35]. As well as helping to elicit the public’s preferences for different potential outcomes, opinion surveys could seek views both on whether the private purchase of a vaccine should be prohibited and on whether the use of lotteries among equally deserving candidates for the vaccine is an acceptable mechanism. A process of public engagement would provide governments with a firmer basis for making allocation decisions involving value judgements.
Timeframes for conducting health economic research will be short. As well as developing clear criteria upon which to base allocation, many practical issues regarding roll-out implementation will also need to be resolved before results of a vaccine RCT are known. In the race for an effective COVID-19 vaccine, health economists need to be ready to take the baton by rapidly developing an evidence-based mechanism for prioritising access.
Declarations
Funding
This article was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (University of Oxford [NIHR-BRC-1215-20008]). LSJR, JB and PMC are supported by the Oxford NIHR Biomedical Research Centre, Oxford, UK. LSJR PMC and FB are supported by the Medical Research Council (UK-Malaysia: Joint Partnership Call on Non- Communicable Diseases Grant Reference: MR/T018593/1).
Conflict of interest
Laurence S. J. Roope, John Buckell, Frauke Becker, Paolo Candio, Mara Violato, Jody L. Sindelar, Adrian Barnett, Raymond Duch and Philip M. Clarke have no conflicts of interest to report.
Open Access
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creat iveco mmons .org/licen ses/by-nc/4.0/.
Philip M. Clarke
Philip.Clarke@ndph.ox.ac.uk
- Health Economics Research Centre, Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
- Department of Health Policy and Management, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, CT, USA
- School of Public Health and Social Work, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
- Nuffield College, University of Oxford, Oxford UK
- Centre for Health Policy, Melbourne School of Population and Global Health, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
References
- Athey S, Kremer M, Snyder C, Tabarrok A. In the race for a coronavirus vaccine, we must go big. really, really big. New York Times. 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/05/04/opinion/coronavirus-vaccine.html. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Coy P. Pay attention to nobel laureate michael kremer on the pandemic. Bloomberg Quint. 2020. https ://www.bloombergquint.com/businessweek/pay-attention-to-nobel-laureate-michael-kremer-on-the-pandemic. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Folegatti PM, Ewer KJ, Aley PK, Angus B, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;396(10249):467–78.
- Terry M. AstraZeneca aims for 30 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine for UK by September. https://www.biospace.com/article/astrazeneca-plans-30-million-university -of-oxford-covid-19-vaccine-doses-by-september/. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Herper M. AstraZeneca lays out plan for producing 2 billion doses of Covid-19 vaccine, if it works. STAT. 2020. https ://www.statnews.com/2020/06/04/astrazeneca-lays-out-plan-for-producing-2-billion-doses-of-covid-19-vaccine-if-it-works/. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Torjesen I. Pre-purchasing vaccine—sensible or selfish? BMJ. 2020;370:m3226. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3226 .
- Adams B. COVID-19 vaccine leaders talk up the need for partners, potential for a working vax by October. Fierce BioTech. https ://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/covid-19-vaccineleaders-talk-up-need-for-partners-potential-for-a-working-vax-by-october. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Mahase E. Covid-19: Oxford team begins vaccine trials in Brazil and South Africa to determine efficacy. BMJ. 2020;369:m2612.
- Kupferschmidt K. ‘Vaccine nationalism’ threatens global plan to distribute COVID-19 shots fairly. 2020. https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/07/vaccine-nationalism-threatens-global-plan-distribute-covid-19-shots-fairly. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- DeRoo SS, Pudalov NJ, Fu LY. Planning for a COVID-19 vaccination program. JAMA. 2020;323(24):2458–9. https://doi. org/10.1001/jama.2020.8711.
- Yamey G, Schäferhoff M, Hatchett R, Pate M, Zhao F, McDade KK. Ensuring global access to COVID-19 vaccines. Lancet. 2020;395(10234):1405–6.
- World Health Organization. More than 150 countries engaged in COVID-19 vaccine global access facility. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/detai l/15-07-2020-more-than-150-countries-engaged-in-covid-19-vaccine-global-access-facility. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Cohen J. The line is forming for a COVID-19 vaccine. Who should be at the front? 2020. https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2020/06/line-form ng-covid-19-vaccine-who-should-be-front. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- National Academy of Medicine, Engineering and Science. A framework for equitable allocation of vaccine for the novel coronavirus. https://www.nationalacademies.org/our-work/a-framework-for-equitable-allocation-of-vaccine-for-the-novel-coronavirus. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Bollyky TJ, Gostin LO, Hamburg MA. The equitable distribution of COVID-19 therapeutics and vaccines. JAMA. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6641 (Epub 7 May 2020).
- Barnhard A. Language more normally suited to wartime is commonly invoked around the Covid-19 pandemic, but can we learn anything from past conflicts in our battle against coronavirus? https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20200 430-covid-19-what-we-can-learn-from-wartime-efforts. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Nevins J. The imperative of personal sacrifice, today and during World War II. New York Times. 2020. https ://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/03/magazine/personal-sacri fice-coronavirus-world-war-ii.html. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Department of Health and Social Care. Cost-Effectiveness Methodology for Immunisation Programmes and Procurement (CEMIPP) Report: the government’s decision and summary of consultation responses. Department of Health and Social Care; 11 Jun 2019.
- Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation. Code of Practice June 2013. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/ government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment data/file/224864/JCVI_Code_of_Practice_revision_2013_-_final .pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation. Independent report: interim advice on priority groups for COVID-19 vaccination. https://www.gov.uk/government /publications/priority-groups-for-coronavirus-covid-19-vaccination-advice-from-thejcvi/interim-advice-on-priority-groups-for-covid-19-vaccination. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Bonaccorsi G, Pierri F, Cinelli M, Flori A, Galeazzi A, Porcelli F, et al. Economic and social consequences of human mobility restrictions under COVID-19. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(27):15530.
- Bärnighausen T, Bloom DE, Cafiero-Fonseca ET, O’Brien JC. Valuing vaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(34):12313–9.
- Sattar N, Ho FK, Gill JMR, Ghouri N, Gray SR, Celis-Morales CA, et al. BMI and future risk for COVID-19 infection and death across sex, age and ethnicity: preliminary findings from UK biobank. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(5):1149–51.
- Briggs A. Estimating QALY lossess associated with deaths in hospital (COVID-19) [research note]. Avalon Health Economics. https://avalonecon.com/wp-conte nt/uploads/2020/04/COVID-19-QALYs-v3.pdf Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- Brotherhood L, Kircher P, Santos C, Tertilt M. IZA DP no. 13265: an economic model of the COVID-19 epidemic: the importance of testing and age-specific policies. Bonn: IZA Institute of Labor Economics; 2020.
- Eichenbaum MS, Rebelo S, Trabandt M. The macroeconomics of epidemics. NBER working paper no. 26882; 2020.
- Glover A, Heathcote J, Krueger D, Rios-Rull JV. Health versus wealth: on the distributional effects of controlling a pandemic.’ Mimeo. 2020. https://www.jonathanheathcote.com/healthwealth.pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- van Doorslaer E, Masseria C; the OECD Health Equity Research Group Members. Income-related inequality in the use of medical care in 21 OCED countries. OECD health working paper no. 14; 2004.
- Cookson R, Drummond M, Weatherly H. Explicit incorporation of equity considerations into economic evaluation of public health interventions. Health Econ Policy Law. 2009;4(2):231–45.
- Hansen P, Devlin N. Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) in healthcare decision-making. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2019.
- Duncan NT. Immigration policymaking in the global era. New York: Palgrave Macmillan; 2012.
- Neumann-Böhme S, Varghese NE, Sabat I, Barros PP, Brouwer W, Exel J, et al. Once we have it, will we use it? A European survey on willingness to be vaccinated against COVID-19. Eur J Health Econ. 2020;21:977–82.
- Kolata G. Who gets the Covid-19 vaccine first? Here’s one idea. New York Times. 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/07/23/health/coronavirus-vaccine-allocation.html. Accessed 12 Aug 2020.
- White DB, Angus DC. A proposed lottery system to allocate scarce COVID-19 medications: promoting fairness and generating knowledge. JAMA. 2020;324(4):329–30.
- Soekhai V, de Bekker-Grob EW, Ellis AR, Vass CM. Discrete choice experiments in health economics: past, present and future. PharmacoEconomics. 2019;37(2):201–26.






